Beneficial electrification has become a popular marketing theme among energy utilities and cooperatives, but the concept is still unfamiliar to many customers. Don’t let that get in the way of communicating this powerful message about the benefits of electrification. The term may be a mouthful, but beneficial electrification can improve customers’ lives in a variety of ways.
To fully communicate the benefits of electrification, energy utilities must answer their customers’ questions, which can range from the most basic definition of beneficial electrification to how they can electrify their homes and businesses once they determine it’s a good fit for them.
Here we break down the most common questions and how you can better equip both residential and business customers with the knowledge they need to make smarter energy choices.
What is Beneficial Electrification?
Beneficial electrification is the process of replacing the direct use of fossil fuels with electricity to reduce overall emissions and energy costs. When consumers switch to electricity — such as replacing a heating oil furnace with an electric heat pump or switching from a gasoline-powered car to an electric vehicle — they benefit through cost savings, convenience and a cleaner environment.
Utilities should make the benefits of electrification clear to customers with regular reminders and marketing campaigns. But remember, your customers likely do not know what beneficial electrification means. You may want to use more relatable phrases in your messaging to capture their attention.

Beneficial electrification is more than fuel switching. Fuel switching is a short-term solution, where beneficial electrification is a long-term approach to replacing fossil fuels. A good way to determine if an initiative meets beneficial electrification standards is to consider the following conditions:
For customers, think about:
- Does it save them money?
- Is it good for the environment?
- Does it improve their quality of life?
When it comes to your utility, think:
- Does it improve the reliability or efficiency of the grid?
It will meet beneficial electrification standards if it can satisfy one of these conditions without adversely affecting the others.
What Can Be Electrified?
Beneficial electrification is most often applied to transportation, space heating, cooking and water heating. For utilities and co-ops, this is where content marketing can help connect the dots.
For residential customers, it’s essential to illustrate the switch to electric vehicles, electric lawnmowers, heat pumps, induction stovetops and other residential appliances. For commercial customers, facility electrification such as process technologies, electric forklifts and other equipment are more relevant.
How Does Beneficial Electrification Save Money?
Electrifying systems, devices and more can help utility customers lower their energy bills. While electrification will typically result in higher electric bills, significant savings can be achieved elsewhere, such as customers’ vehicle fuel bills. “Reducing energy spend” may be a more accurate phrase to describe the overall financial benefits of electrification.
However, the cost of electricity itself is a barrier. For example, potential EV purchasers may have the perception that gas is cheaper, which is true in some cases. They need to get past the cost of a gallon of gas (or a kilowatt-hour) to see how electric vehicles are much more efficient than internal combustion engines overall, not to mention that EVs come with lower maintenance costs. EV owners will save about $1,000 per year on fuel, with total cost-of-ownership savings of up to $10,000 over the life of an EV.
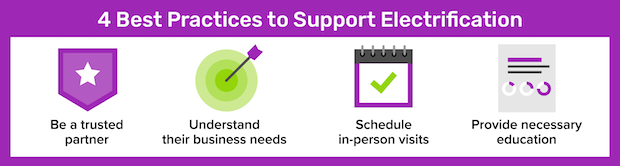
Share helpful content that gives your customers step-by-step suggestions to electrify their homes and businesses. Getting valuable advice from a trusted source can make them feel more comfortable and confident as they begin the long electrification process.
Does Beneficial Electrification Help the Environment?
Electricity gets cleaner every day, with more of the nation’s supply being generated from renewable sources. For example, carbon dioxide emissions per megawatt hour from electric power generation decreased 36% from 2005 to 2021. By driving the transition away from fossil fuels, beneficial electrification is having a major impact on the environment.
EVs are a great example of beneficial electrification. Electric vehicles have zero tailpipe emissions and reduce well-to-wheels emissions by at least 20%. Electric power generated by renewables adds to that advantage — ultimately up to 100% reduction in carbon emissions.
Aren’t Fossil Fuels Used to Generate Electricity?
A big point of confusion in the conversation about electrification surrounds the idea of what it means to truly “go green.” Although we are slowly transitioning to clean, renewable power generation, fossil fuels are still burned to produce electricity. So, although they’re “going electric,” some customers are concerned that it may not be enough — or even “count” — if it still requires the use of harmful fossil fuels.
However, beneficial electrification doesn’t require that 100% of their electricity come from clean energy sources. New electric-powered equipment and appliances are much more energy-efficient than the devices they replace.
Heat pump efficiency has risen from 10 SEER (seasonal energy efficiency ratio) to close to 20 SEER — that’s 500% efficient! — for cooling, and from 6 HSPF (heating seasonal performance factor) to 10 FSPF — 250% efficient! — for heating in a couple of decades. Natural gas furnaces are 92% efficient.
In the short term, the consumer is reducing their overall energy use by upgrading to a new electric appliance; in the long term, that electricity will come from increasingly green sources.
What Are the Benefits of Electrification?
There are many benefits to electrification, ranging from helping residential customers save energy to supporting a cleaner, more resilient grid for their community. Other benefits of electrification include:
- Reduced emissions
- Grid-connected appliances and systems
- Increased efficiency
- Reduced likelihood of power outages
- Decreased maintenance costs
- Reduced operating costs
- Minimal interruptions with energy storage
There are also application-specific benefits of electrification, including:
- Induction cooktops heat food more quickly
- Electric vehicles lower the operating costs of fleets
- Heat pumps are quieter, more efficient and require less maintenance
- Smart technology can make life easier by connecting devices
- Electric lawn tools don’t require potentially dangerous fuel storage
Communicating the benefits of electrification to your customers with specific examples shows them how beneficial electrification can impact and improve their daily lives.
What Are the Barriers to Electrification?
Though the expected benefits may be enough to get your customers intrigued, there are a few barriers to beneficial electrification residential and business customers may encounter, including:
- The low cost of natural gas
- Range anxiety for electric vehicles
- Increased capital cost for electric equipment
- Lack of customer awareness of alternative electric technologies
- Lack of trained installers and repair technicians for advanced technologies like variable-refrigerant flow HVAC and heat pump water heaters
- Misconceptions that industrial equipment like electric forklifts are underpowered and batteries cannot last a full shift
- Safety concerns for electric lift trucks in wet weather conditions
Despite these hurdles, beneficial electrification can save customers money, reduce emissions and improve quality of life, all without negatively impacting the grid.
With these benefits in mind, it’s clear that customers are going to become more interested in beneficial electrification options and will look to their utility as a resource for better managing their energy use. That’s why it’s imperative to be ready with content and answers to any questions they may have as they begin their electrification journey.